If you run a digital product, agency, or e-commerce business, learning how to build your own chatbot is no longer a nice side project. It’s a direct way to cut support costs, capture more leads, and keep customers engaged 24/7.
Market reports heading into 2025 show conversational AI spend growing at double‑digit rates every year. At the same time, customer surveys through 2023–2024 consistently show that well over half of buyers now expect fast, on‑site chat or messaging support as standard.
The good news: you don’t need a PhD in AI to build your own chatbot anymore. With the right plan, you can launch a useful bot in weeks, not months – whether that’s a website widget, a Slack assistant, or a voice bot that answers your phone.
This guide walks you through:
- What a modern chatbot actually is (beyond the buzz)
- The business case, with realistic numbers
- No‑code vs. developer builds (and where tools like NewOaks fit in)
- A practical step‑by‑step process to build your own chatbot
- Text and voice bot examples you can copy
- How to roll it out, promote it, and avoid common mistakes
What a Modern Chatbot Actually Is
Before you build your own chatbot, you need to be clear on what you’re building.
Standard Chatbots vs. AI Chatbots

Standard (rule‑based) chatbots
- Follow decision trees and prewritten scripts
- Reply based on keywords, buttons, and simple “if this, then that” logic
- Break easily when users go off script
Classic tools like Botsify, Chatfuel, Hubspot Bot Builder, and Typebot grew up around this model – especially for Facebook and Slack bots.
AI chatbots
- Use Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU), and Machine Learning (ML)
- Rely on large language models (LLMs) to understand intent instead of just keywords
- Can respond in free text, handle follow‑ups, and keep context
- Learn and improve as you feed them more data and review conversations
In practice, the best setups in 2026 mix both: AI chatbots for flexible conversation and rules for high‑risk flows like payments or compliance steps.
“The most effective chatbots don’t replace humans; they reserve people for the conversations that matter most.” – advice often shared by support and success leaders
Text Bots vs. Voice Bots

You can build your own chatbot in two main flavors:
- Text‑based bots
- Website widgets
- In‑app chat
- Messaging apps (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Slack)
- Voice‑based bots
- Phone numbers that answer with speech (IVR replacement)
- Smart speaker skills
- In‑app voice assistants
Under the hood, voice bots add speech‑to‑text and text‑to‑speech on top of the same AI models a text bot uses. You design the logic once, then expose it over text, voice, or both.
Why Building Your Own Chatbot Is Worth It
If you’re going to build your own chatbot, you should know what a “win” looks like.
The Business Case (With Realistic Numbers)

From what product teams, agencies, and SaaS report publicly, well‑executed bots often deliver results like:
- Support deflection: 20–40% of simple tickets handled fully by the bot within a few months
- Response time: Common questions answered instantly instead of in hours
- Lead capture: 2–3x more leads vs. passive contact forms, because a bot starts the conversation
- Sales efficiency: Fewer unqualified demos; sales only speaks with users who passed basic fit checks
Analyst forecasts through 2024–2025 also point in the same direction: double‑digit yearly growth in conversational AI and chatbots, driven largely by cost pressure on support teams and rising customer expectations for always‑on help.
“Start narrow, measure everything, then expand.” – common playbook among teams that see real ROI from chatbots
How Chatbots Change Your Workflow
Once you build your own chatbot and plug it into your daily operations, you can:
- Let the bot handle FAQs, status checks, and simple account questions
- Use human agents only for edge cases and high‑value conversations
- Turn every chat into a chance to capture email, phone, and intent data
- Feed those insights back into product, marketing, and onboarding
Instead of more headcount every time volume spikes, you add better conversation flows and more training data.
Decide Your Approach: No‑Code, Low‑Code, or Developer Build

There are three main ways to build your own chatbot in 2026. Pick the one that matches your resources and ambition.
1. No‑Code Platforms (Fastest Way to Start)
Best for:
- WordPress business owners and agencies
- Small teams, marketing departments, solo founders
- Anyone who wants results fast without engineering help
Typical features:
- Visual drag‑and‑drop flow builder
- Upload or crawl your content to train the bot
- Website widget + messaging channels from one dashboard
- Built‑in analytics, lead capture, and basic integrations
Where NewOaks Fits
Tools like NewOaks focus on connecting AI to your real business data and workflows so you can build your own chatbot that:
- Answers questions from your docs, site, and knowledge base
- Routes leads and support requests to the right person or system
- Runs repeatable “mini‑processes” (qualification, onboarding steps, simple troubleshooting)
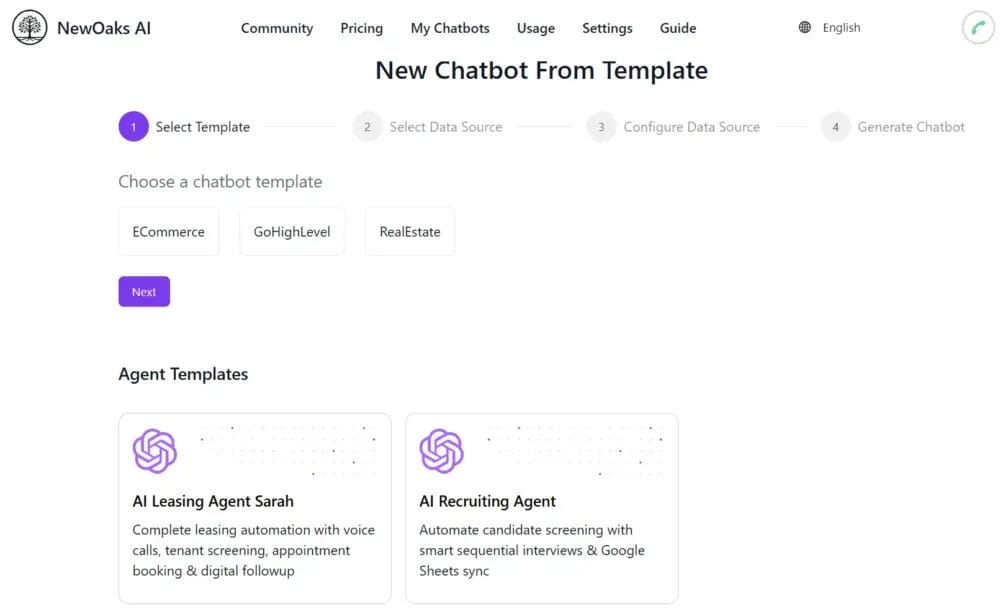
Think of this as a practical way for a non‑technical founder to ship a useful chatbot instead of a toy.
2. Low-Code / Technical Marketer Setup
Best for:
- Teams with one or two technical people comfortable with APIs and webhooks
- Businesses that need deeper integrations but don’t want a full custom build
Here you might:
- Use a no‑code platform as the front end
- Add custom functions with serverless code
- Call external APIs (pricing, shipping, internal tools)
- Push data into CRMs, helpdesks, and data warehouses
This is often the sweet spot for growing SaaS and e‑commerce brands.
3. Full Developer‑Focused Build
Best for:
- Enterprises
- Financial services, healthcare, or consulting firms with strict compliance
- Products where the chatbot is the core of the offering
Here your team might use:
- Raw APIs from LLM providers
- Frameworks and SDKs
- Your infrastructure and data pipelines
Older frameworks like HubSpot Chatbot Builder, TypeBot, and newer conversational AI stacks gave developers this kind of control, especially for Slack and Messenger bots.
This route takes longer and costs more, but you get deeper control over behavior, data, and security.
Step‑By‑Step: How To Build Your Own Chatbot From Scratch
Let’s get practical. This is a straightforward path you can follow, whether you choose NewOaks, another no‑code tool, or a dev stack.
Step 1: Pick A Sharp, Narrow Use Case
You do not want a bot that “does everything.”
Start by answering:
- What single problem will this bot solve first?
- For which segment of your target audience?
- What metric will tell you it’s working? (ticket deflection, demo bookings, NPS, etc.)
Examples:
- SaaS: Answer 80% of “How do I…?” questions about a new feature
- E‑commerce: Track orders, answer shipping questions, handle simple returns
- Agency: Qualify leads on the site and send only good fits to your sales calendar
Step 2: Choose Your Channels
Next, decide where people will meet your bot. Common options:
- Website widget (default for most businesses)
- In‑product chat for SaaS
- Messaging platforms:
- Slack – internal team assistant or B2B product companion
- Facebook Messenger – consumer brands and communities
- Instagram – some youth‑focused and entertainment use cases
You can start with one channel, then expand. Many platforms were created precisely to bridge bots into apps like Instagram, Slack, or Messenger without rewriting everything.
Step 3: Design Personality and Tone
Even if you build your own chatbot mainly for efficiency, humans still interact with it.
Decide:
- Formal vs. casual voice
- Short, direct answers vs. more “chatty” text
- Use of emojis or not (often fine for DTC, not for banking)
Examples:
- A finance app should be calm, precise, and formal
- A beauty brand can be playful and friendly
- A B2B SaaS bot can be clear and professional with a light personality
Keep it consistent across replies and error messages.
Step 4: Map the Conversation Flows

AI models can improvise, but you still need structure.
Sketch:
- Entry points: “Hi, how can I help you?” plus suggested quick replies
- Main flows:
- Answer FAQs
- Qualify a lead
- Book a demo or call
- Check order or subscription status
- Escalation: when and how the bot hands over to a human
Keep flows short and focused. If a task takes more than 6–8 steps, either simplify it or send it to a human.
Step 5: Pick Your Platform and Stack
Now tie steps 1–4 to specific tech.
You might:
- Use a no‑code tool like NewOaks for:
- Training on your docs and site
- Setting up flows for lead capture and support
- Integrations with your existing tools
- Or rely on chatbot builders such as:
For multi‑channel bots, a connector like NewOaks can sit in the middle, linking your logic to Slack, Instagram, or Messenger.
Step 6: Train the Bot on Your Content
This is where a “dumb” bot becomes useful.
Feed it:
- Help center and knowledge base articles
- Onboarding guides and SOPs
- Product specs, FAQs, and policy pages
- Internal docs (for internal bots)
Most modern tools let you:
- Upload PDFs, DOCX, and text files
- Point the bot at your site so it crawls pages automatically
- Add specific Q&A pairs to correct or override answers
In 2024 and beyond, many platforms use retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG) in the background. That means the bot looks up relevant chunks of your content first, then uses the AI model to write a clear answer from those chunks.
Step 7: Connect to Your Systems
To move beyond a “fancy FAQ,” build your own chatbot so it can act, not just answer.
Examples of connections:
- CRM: create or update contacts and deals
- Helpdesk: open tickets for complex issues
- Email marketing: add people to the right list or segment
- Calendars: book sales calls or onboarding sessions
- Internal tools: fetch account limits, usage, or billing status
Many no‑code platforms offer out‑of‑the‑box integrations. With low‑code, you can add webhooks and custom functions to call your APIs.
Step 8: Test With Real People (Not Just Your Team)
Do not skip this step.
Run:
- Internal tests with your team across devices and channels
- A small private beta with friendly customers or partners
- Edge‑case tests: typos, slang, weird phrasing, frustrated users
Look for:
- Wrong or outdated answers
- Loops where users get stuck
- Points where the bot should escalate sooner
Make it easy for testers to send comments directly from the chat. Gather and act on that feedback quickly.
Step 9: Launch, Promote, and Measure
Once your chatbot is stable, get it in front of people.
Ways to promote:
- Website:
- Add the widget across key pages (pricing, docs, checkout)
- Add a short line above the fold: “Questions? Ask our chatbot.”
- Email:
- Add a “Chat with us” link in signatures and campaigns
- Content and SEO:
- Create a short landing page describing what the bot does
- Use solid on‑page SEO so people can find it – this guide on using SEO to attract users is a good starting point
- Directories and communities:
- If you have a Messenger or Slack bot, submit it to their app directories
- Share it in relevant groups where your audience hangs out
Track at least:
- Number of conversations
- Completion rate of key flows (e.g., “demo booked,” “order tracked”)
- Percent of chats resolved without human help
- CSAT or simple thumbs-up/thumbs-down on answers
Use this data to decide what to improve next.
Practical Examples: Text and Voice Chatbots You Can Actually Build
Here are concrete patterns you can adapt instead of starting from a blank page.
1. SaaS Onboarding Bot (Text)
Channel: Website + in‑app widget
Audience: New trial users
What it does:
- Welcomes new users and asks what they’re trying to achieve
- Offers 3–5 guided paths (e.g., “Set up my first campaign”)
- Answers “How do I…?” feature questions from your docs
- Suggests next steps based on activity
- Books a call with customer success for stuck high‑value users
Result: Faster time‑to‑value for new users and fewer repetitive onboarding tickets.
2. E‑Commerce Sales & Support Bot (Text)
Channel: Website, Messenger, maybe Instagram DMs
What it does:
- Asks a few questions to recommend products (budget, use case, preferences)
- Answers questions on shipping, returns, sizing, and materials
- Tracks orders based on email or order number
- Initiates simple returns or exchanges
- Collects email or SMS consent for follow‑ups
Result: More conversions from existing traffic and lower support load during busy seasons.
3. Service Business Voice Bot (Phone)
Channel: Phone number with voice bot on the front line
Audience: Prospects and existing clients
What it does:
- Answers calls 24/7 with a natural‑sounding greeting
- Asks why the caller is contacting you and routes based on intent
- Collects basic details (name, company, phone, email, short description)
- Books time on a consultant’s calendar for qualified prospects
- Plays status updates or FAQs for existing clients
Result: Fewer missed calls, better qualification, and a calmer team.
You can build your own chatbot for any of these patterns with a no‑code platform and some careful flow design.
Essential Features Checklist for a 2026-Ready Chatbot
When you pick tools to build your own chatbot, make sure they hit these basics.
Core AI and Conversation
- Quality AI model with strong language understanding
- Support for retrieval from your docs and site (not just generic internet knowledge)
- Context handling across multiple turns in a conversation
- Clear way to override or correct answers
Business and Marketing Features
- Built‑in lead capture (forms, consent, tags)
- Easy connections to CRMs, helpdesks, and email tools
- Website and multi‑channel deployment from one place
Operations and Reliability
- Analytics dashboard with:
- Conversation volume
- Resolution vs. escalation rate
- Common questions and intents
- Exportable conversation logs for review and training
- Ability to grow with more users without falling over
Security and Compliance
- Clear data handling policy
- Encryption in transit and at rest
- Controls over what data is sent to AI models
- Features that help you meet your industry’s compliance needs
Platforms like NewOaks and others in this space focus heavily on data control and process design, which matters a lot once your chatbot touches customer or financial information.
Common Mistakes When You Build Your Own Chatbot
Avoid these traps; they waste time and erode trust.
- Trying to Do Everything at Once
Start with one clear use case and win. You can add more flows later. - No Clear Owner
Someone on your team must “own” the bot: reviewing chats, updating content, and watching metrics. - Hiding Limitations
Always tell users they’re talking to a bot and make it easy to ask for a human. - Set‑And‑Forget Mindset
The first version is the worst version. Plan weekly or monthly review cycles to improve. - Ignoring Channel Fit
What works in Slack for your team will not feel right in Messenger for consumers. Adjust greeting, length, and tone.
“Good chatbots are written, not just configured.” – reminder that conversation design is an ongoing content job, not a one‑time setup
Bringing It All Together
If you run a startup, agency, or online store and you still don’t build your own chatbot, you’re leaving money and time on the table.
A focused chatbot can:
- Answer common questions instantly
- Cut support volume
- Capture and qualify more leads
- Feed you real language from customers that improves your marketing and product
Start small:
- Pick one use case.
- Choose a no‑code platform such as NewOaks or another tool that fits your stack.
- Train it on your existing content.
- Wire it into your core systems.
- Launch, measure, and improve.
Do that well, and you’ll have a repeatable workflow that scales better than just adding more people to your inbox.
Ready to Build Your Chatbot? Get Expert Help
Building your own chatbot is exciting – but getting from concept to a production-ready bot that actually delivers ROI can feel overwhelming.
Whether you’re just starting out or stuck on deployment, implementation, or optimization, you don’t have to figure it all out alone.
Work With Ruhani Rabin
Ruhani Rabin offers competitive, long-term support for businesses looking to:
- Design and build custom chatbots (text or voice)
- Integrate bots with your existing tools and workflows
- Train and optimize AI models for better accuracy
- Scale chatbot systems as your business grows
- Provide ongoing maintenance and feature updates
With hands-on experience across platforms, industries, and use cases, Ruhani helps you skip the trial-and-error phase and launch a bot that works from day one.
Get in touch today to discuss your chatbot project and get a tailored plan that fits your budget and timeline.
